India’s first solar mission, Aditya-L1, is set to launch in 2nd September 2023 (probably). The mission will study the Sun’s atmosphere, including the chromosphere and corona, in order to better understand its dynamics and evolution. Aditya-L1 will also study the solar wind, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and solar flares.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to embark on a remarkable journey with its inaugural solar mission, Aditya-L1. This mission holds significant promise for advancing our understanding of the Sun and its intricate dynamics.
Named after the Sun, which is also known as “Aditya” in Sanskrit, the Aditya-L1 mission aims to study the Sun’s outermost layer, the corona, and the chromosphere, which lies just below it. This ambitious venture seeks to uncover the mysteries surrounding the Sun’s behavior, such as the causes of its extreme temperature differences and the origins of solar winds and flares.
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft is equipped with cutting-edge instruments to capture crucial data and images of the Sun’s atmosphere. One of the primary tools on board is the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), which will enable scientists to observe the solar corona in visible light and measure the velocity of ejected material.
Additionally, the Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) will analyze the composition and variations in solar wind, contributing to our understanding of its impact on Earth’s magnetosphere.
This mission holds immense significance not only for advancing our knowledge of the Sun’s behavior but also for its practical applications. The insights gained from Aditya-L1 could help improve space weather forecasts, which in turn can safeguard vital communication and navigation systems that are susceptible to solar disturbances.
The Aditya-L1 mission is an endeavor to enhance India’s capabilities in space research and exploration, further solidifying ISRO’s reputation as a pioneering space agency. As the mission embarks on its journey to study the Sun from a unique vantage point, scientists and researchers eagerly anticipate the wealth of data and insights it will bring.

Aditya-L1: Pioneering Sun Study from Space
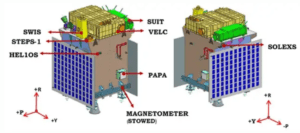
Aditya-L1 marks a significant stride as India’s inaugural space-based mission dedicated to comprehending the Sun. Positioned within a halo orbit encircling the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, approximately 1.5 million km from Earth, this spacecraft reaps the unique advantage of unceasingly observing the Sun without encountering any interruptions like occultations or eclipses. This unobstructed perspective furnishes an unparalleled opportunity to scrutinize solar activities and their ensuing impact on space weather, in real-time. The mission encompasses seven distinct payloads, encompassing electromagnetic, particle, and magnetic field detectors. Their combined efforts aim to dissect the photosphere, chromosphere, and the Sun’s outermost layers, known as the corona.

Through the advantageous vantage point of L1, four of these payloads possess the direct capability to observe the Sun’s dynamics, while the remaining three delve into in-situ studies of particles and fields within the L1 Lagrange point. These investigations hold the promise of offering invaluable insights into the propagatory ramifications of solar dynamics within the interplanetary medium.
The Aditya-L1 payload assemblage is anticipated to yield indispensable data in unlocking the intricacies of coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, pre-flare and flare activities, particle propagation, space weather dynamics, and magnetic field characteristics.

Key Objectives of the Aditya-L1 Mission
The key objectives of the Aditya-L1 mission are to:
- Study the dynamics of the solar atmosphere, especially the chromosphere and corona.
- Understand the heating mechanisms of the chromosphere and corona.
- Study the physics of the partially ionized plasma in the solar atmosphere.
- Investigate the initiation of CMEs and flares.
- Improve our understanding of the Sun-Earth connection.

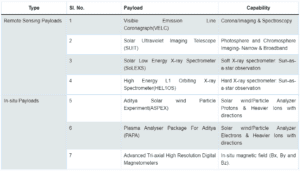
Scientific Payloads of the Aditya-L1 Mission
The overarching scientific objectives of the Aditya-L1 mission encompass:
- Probing the dynamics of the Sun’s upper atmosphere, including the chromosphere and corona.
- Unraveling the intricacies of chromospheric and coronal heating, the physics of partially ionized plasma, the inception of coronal mass ejections, and solar flares.
- Capturing in-situ data about particles and plasma environments to enable an understanding of solar particle dynamics.
- Deciphering the heating mechanism and physics underlying the solar corona.
- Enabling diagnostics of plasma parameters within the coronal and coronal loops, encompassing temperature, velocity, and density.
- Unearthing insights into the development, dynamics, and origins of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- Tracing the sequence of processes spanning various layers—chromosphere, corona base, and extended corona—that culminate in solar eruptive events.
- Elucidating the magnetic field topology and conducting magnetic field measurements within the solar corona.
- Identifying the drivers responsible for space weather, including the origin, composition, and dynamics of solar wind.

Payload Configuration:
Each payload’s distinctive capabilities contribute to a diverse range of scientific investigations…

Launch and Orbit of the Aditya-L1 Mission
Expected Results of the Aditya-L1 Mission

The Aditya-L1 mission marks a significant milestone in ISRO’s space exploration efforts. With its focus on unraveling the mysteries of the Sun’s behavior and its potential to impact our daily lives, this solar mission promises to open new horizons in our understanding of the cosmos.
