On Feb. 3, 1994, space shuttle Discovery took off on its 18th flight, STS-60. Its six-person crew of Commander Charles F. Bolden, Pilot Kenneth S. Reightler, and Mission Specialists N. Jan Davis, Ronald M. Sega, Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, who served as payload commander, and Sergei K. Krikalev of the Russian Space Agency, now Roscosmos, flew the first mission of the Shuttle-Mir Program. Other objectives of the mission included the first flight of the Wake Shield Facility, a free-flying satellite using the ultra-vacuum of space to generate semi-conductor films for advanced electronics and the second flight of a Spacehab commercially developed pressurized module to enable multidisciplinary research and technology demonstrations. The eight-day mission marked an important step forward in international cooperation and the commercial development of space.
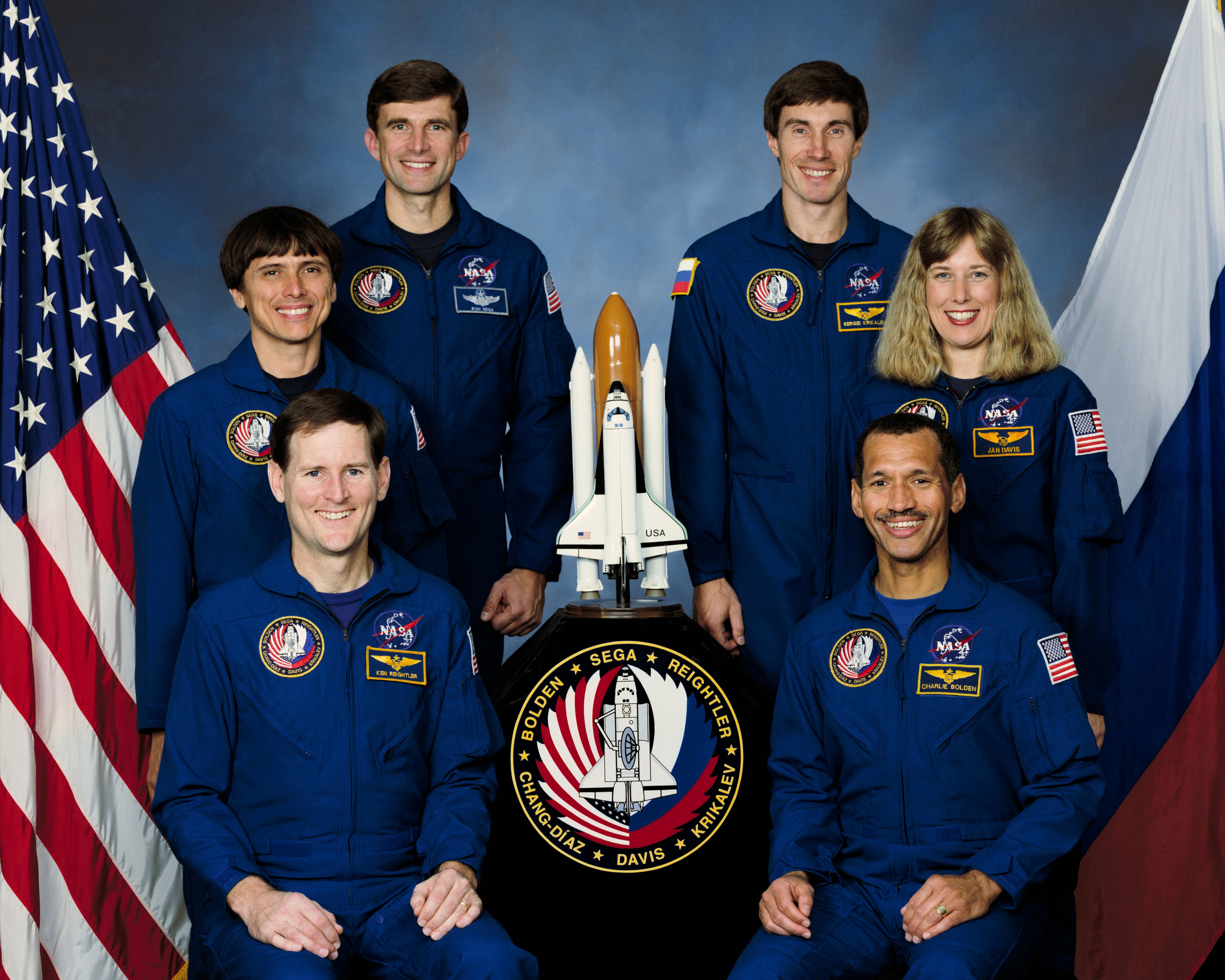



Left: The STS-60 crew patch. Middle: The STS-60 crew of (clockwise from bottom left) Pilot Kenneth S. Reightler, Mission Specialists Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, Ronald M. Sega, Sergei K. Krikalev representing the Russian Space Agency, now Roscosmos, and N. Jan Davis, and Commander Charles F. Bolden. Right: The patch for the Phase 1 Shuttle-Mir program.
In Oct. 1992, NASA announced Bolden, Reightler, Davis, Sega, and Chang-Díaz as the STS-60 crew. For Bolden and Chang-Díaz, STS-60 represented their fourth trips into space; for Bolden the second as commander. Reightler and Davis each had completed one previous spaceflight, with Sega as the sole rookie on the crew. The announcement noted that one of two RSA cosmonauts already in training at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston would join the crew at a later date. In early April 1993, NASA designated Krikalev, a veteran of two long-duration missions aboard the Mir space station, as the prime international crew member, with Vladimir G. Titov named as his backup. The now six-person crew trained extensively for the next nine months for the history-making flight.
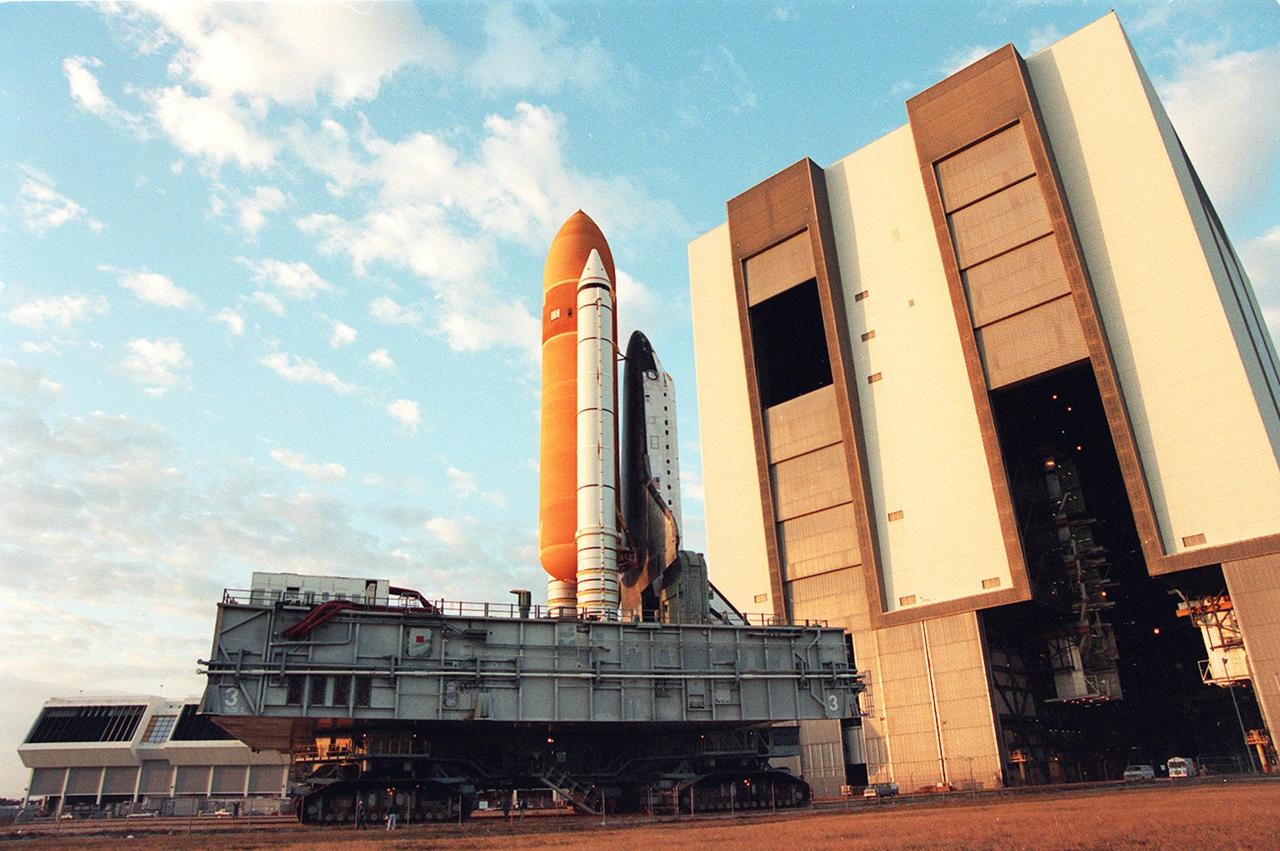
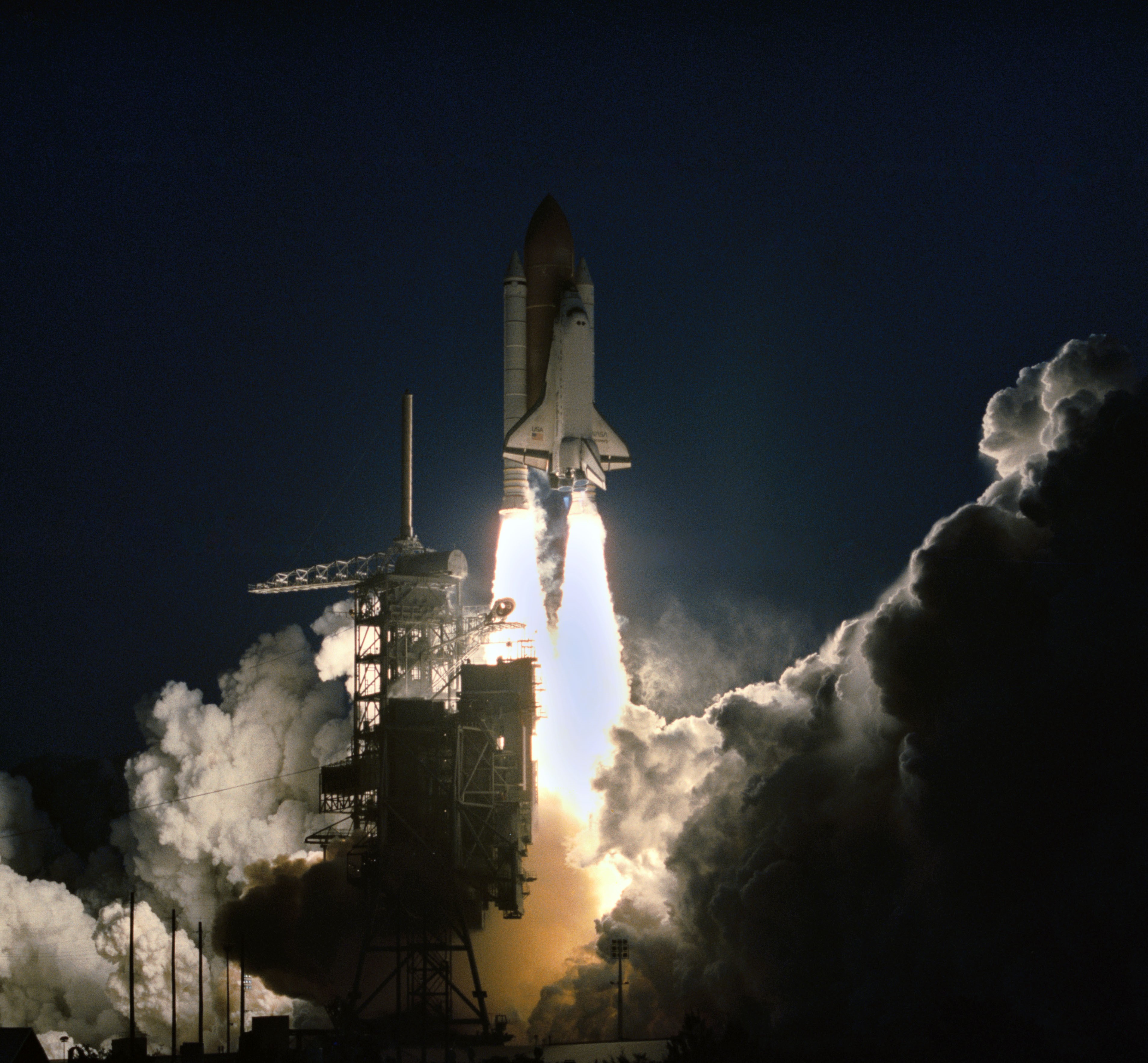



Left: Space shuttle Discovery departs the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Launch Pad 39A. Middle: The STS-60 crew departs crew quarters for Launch Pad 39A. Right: Liftoff of space shuttle Discovery to begin the STS-60 mission.
Discovery landed at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida after its previous mission, STS-51, on Sept. 22, 1993, where workers towed it to the Orbiter Processing Facility to refurbish it for STS-60. They towed it to the Vehicle Assembly Building on Jan. 4, 1994, for mating with its external tank and twin solid rocket boosters, and rolled the completed stack to Launch Pad 39A six days later. The astronauts participated in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, a rehearsal for the actual countdown, on Jan. 14. Senior managers held the Flight Readiness Review on Jan. 22 to confirm the Feb. 3 launch date. Engineers began the countdown for launch on Jan. 31. Liftoff occurred on schedule at 7:10 a.m. EST on Feb. 3, and Discovery and its six-person crew flew up the U.S. East Coast to achieve a 57-degree inclination orbit.
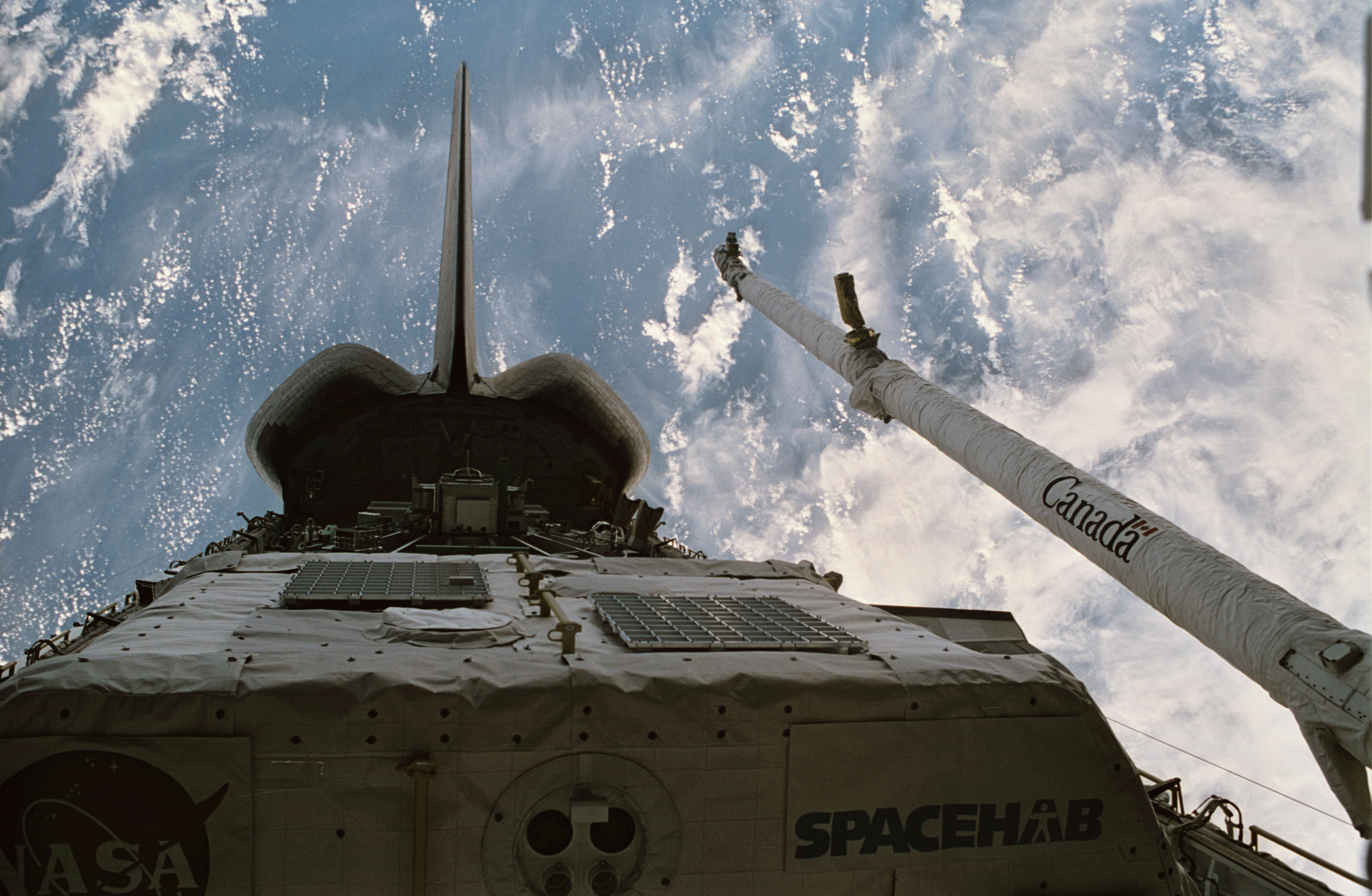
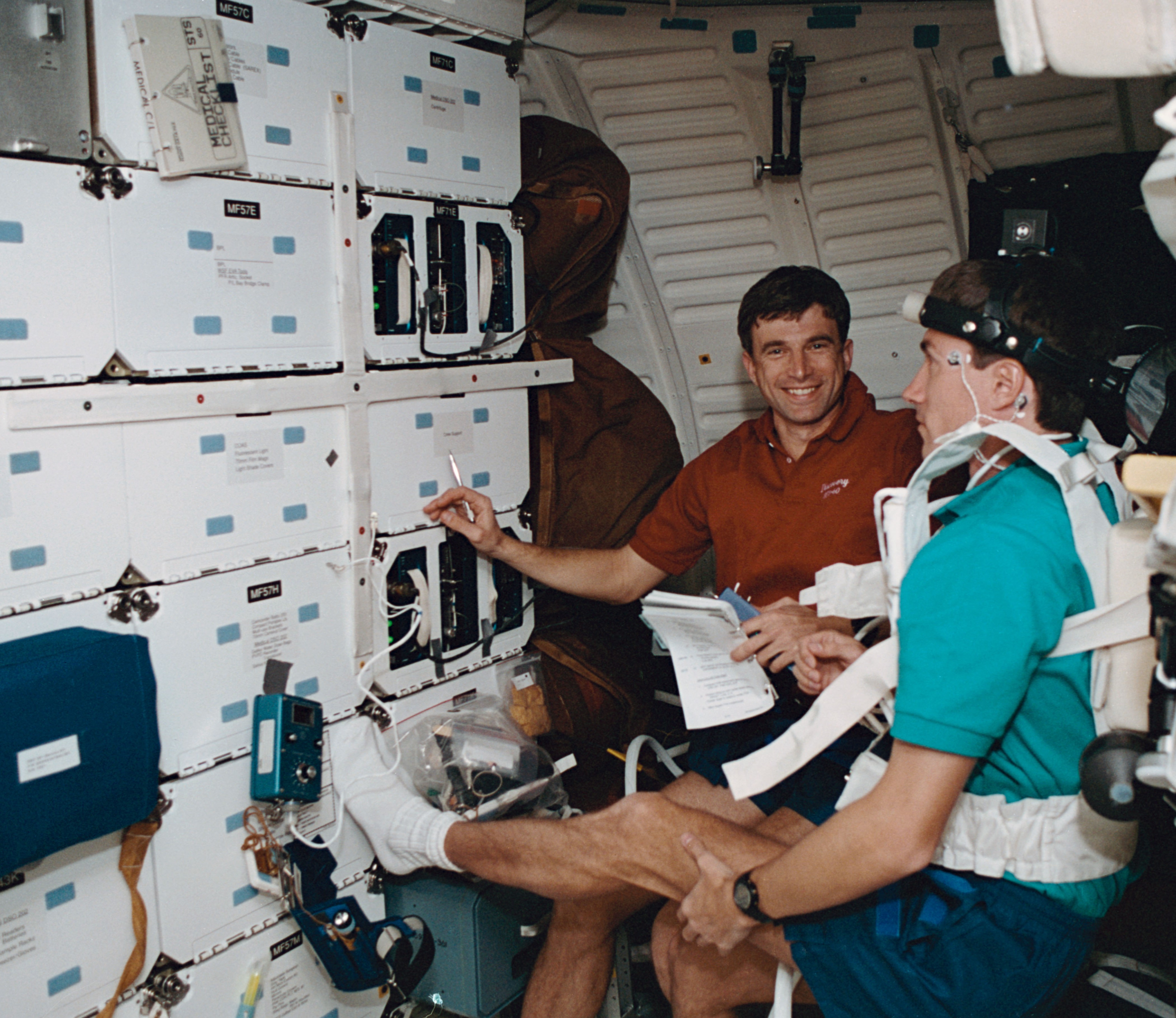

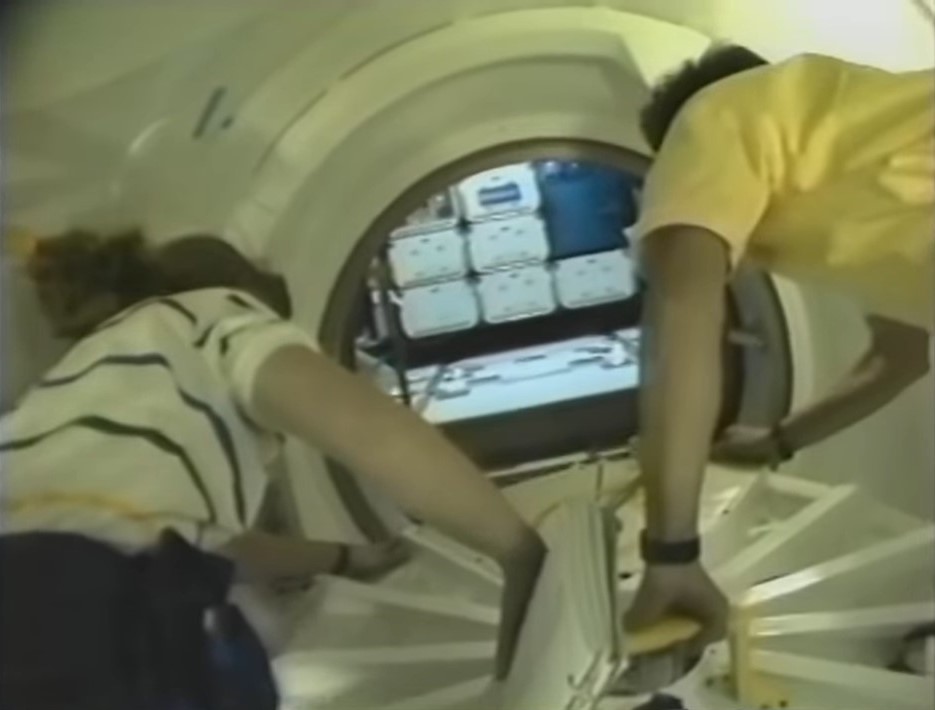

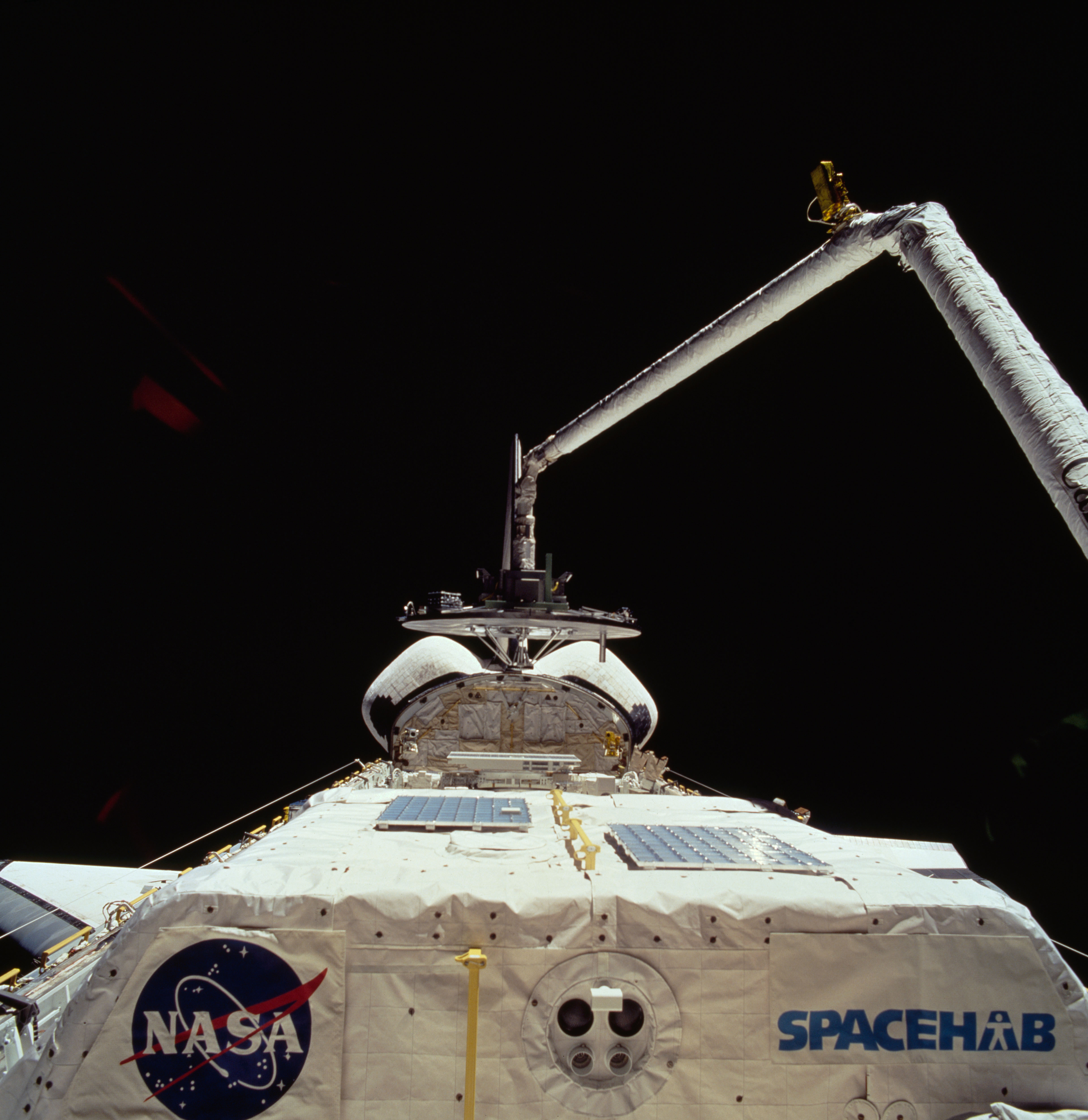
Left: Discovery’s payload bay, showing the Spacehab module including the externally mounted Sample Return Experiment, and the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System. Middle: Astronauts N. Jan Davis, left, and Franklin R. Chang-Díaz open the hatch to the Spacehab module. Right: Ronald M. Sega monitors Sergei K. Krikalev as he performs a neurosensory investigation.
Once in orbit, the astronauts opened Discovery’s payload bay doors to begin their activities. Chang-Díaz and Davis opened the hatches to the Spacehab, accessed from the middeck through the airlock and a connecting tunnel, and activated the module’s systems. They began activating some of the 12 experiments in the Spacehab, primarily focused on biotechnology and materials processing. In the middeck, Reightler, Davis, Sega, and Krikalev performed the first session of the joint neurovestibular experiment, which they repeated five more times during the mission. The astronauts also began activating some of the experiments in the shuttle’s middeck.
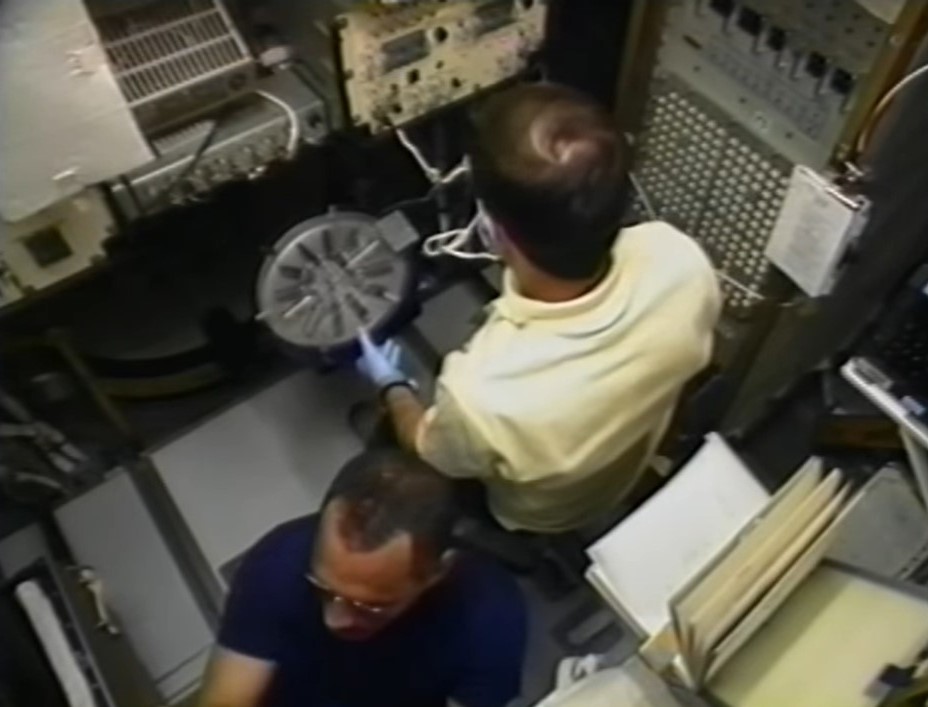
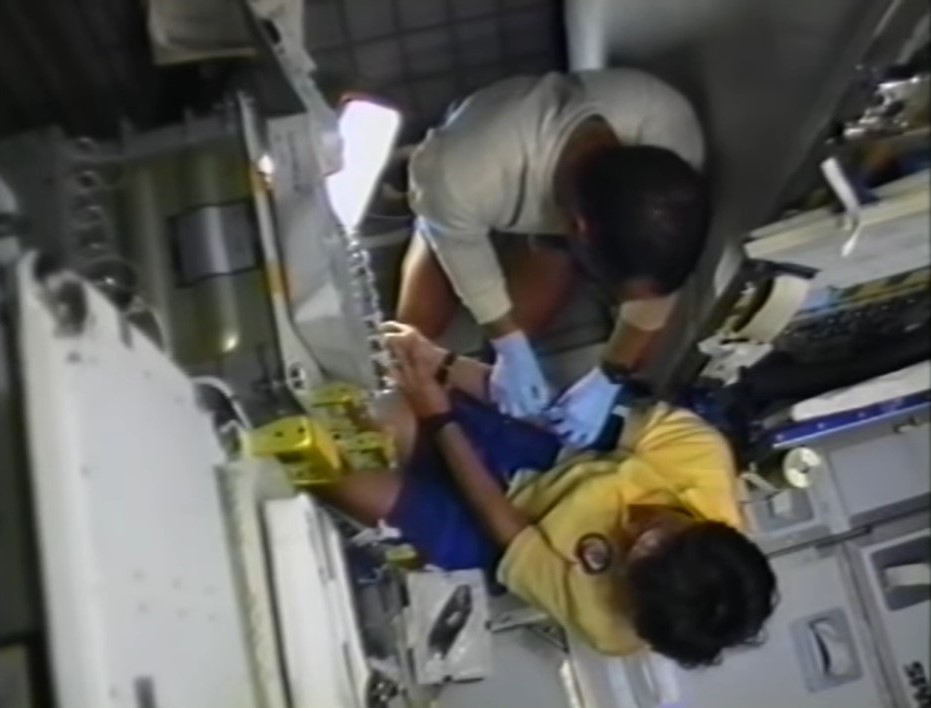


Left: Charles F. Bolden prepares to take a blood sample from Franklin R. Chang-Díaz for the metabolic experiment. Middle: Kenneth S. Reightler processes blood samples in the centrifuge. Right: Reightler places the processed blood samples in the GN2 freezer.
The astronauts began the joint metabolic experiment to investigate biochemical responses to weightlessness on flight day 2. With Bolden and Chang-Díaz serving as phlebotomists, they and Reightler participated as subjects for this study that involved drawing blood samples, spinning them in a centrifuge, and placing them in gaseous nitrogen freezers for return to Earth for analysis.
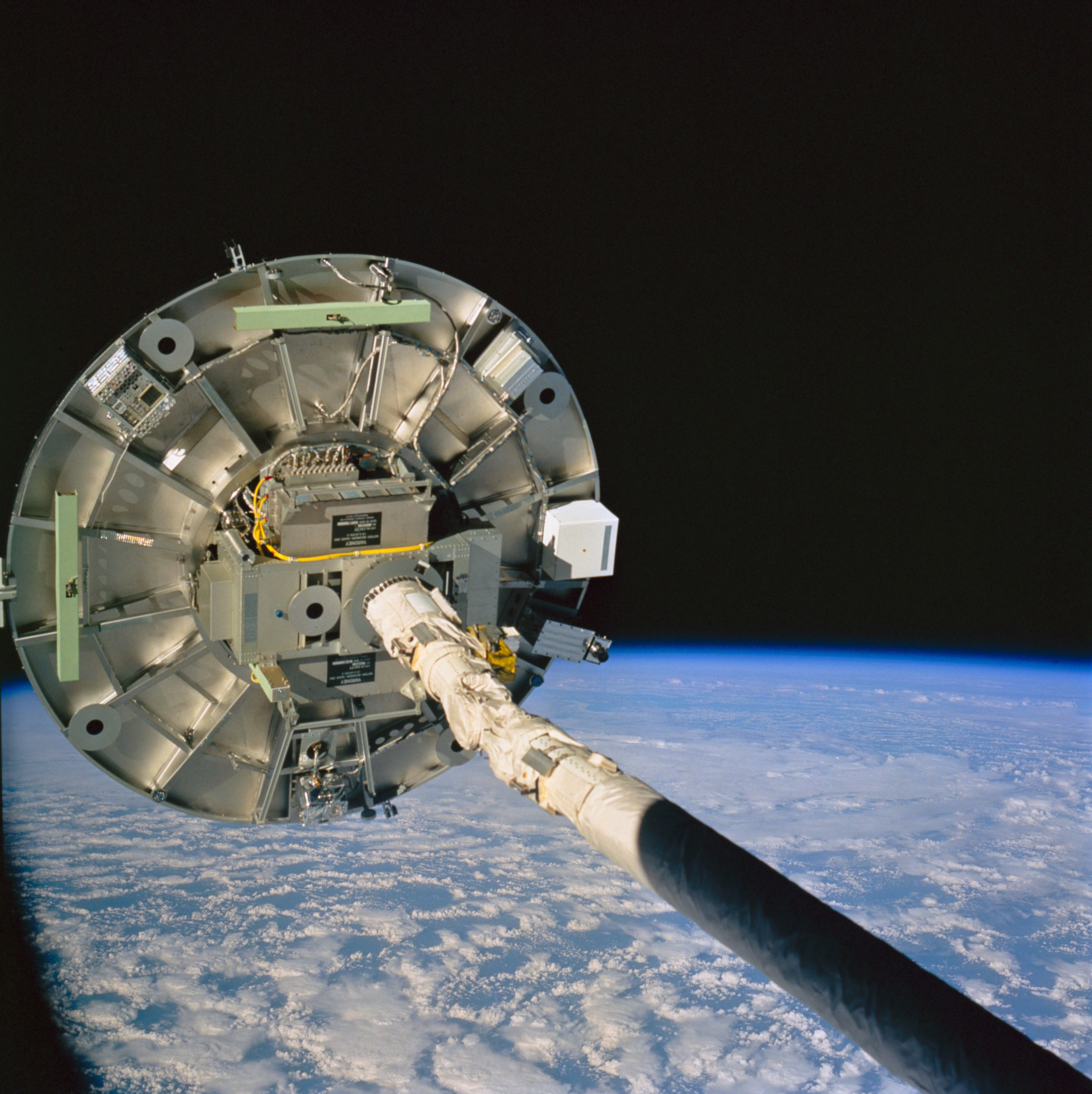
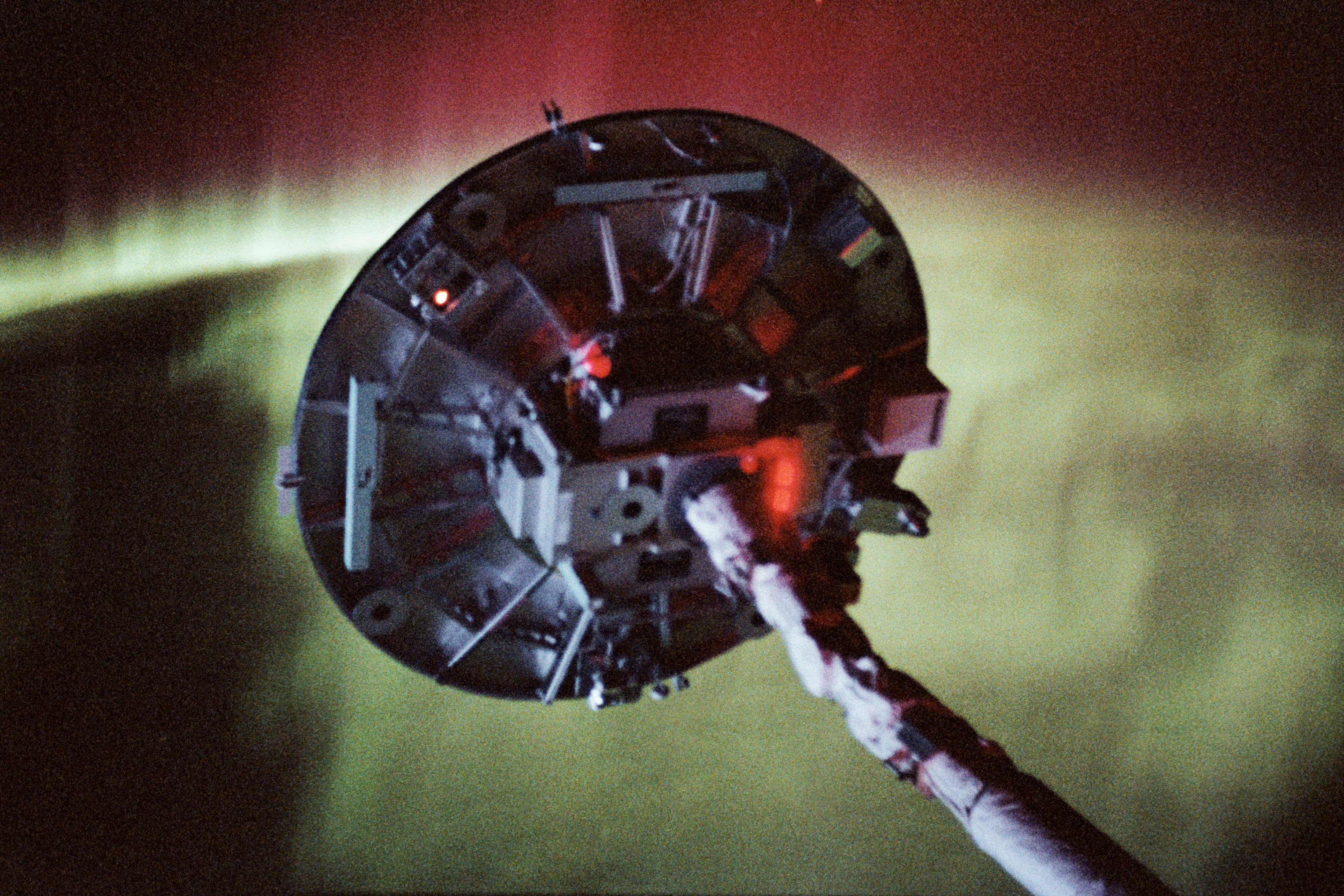


Left: The Wake Shield Facility (WSF) deployed at the end of the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System, with the aurora in the background. Middle: The WSF at the end of the RMS. Right: The robotic arm about to stow the Wake Shield Facility.
Operations with the wake shield began in flight day three. Davis grappled the WSF (Wake Shield Facility) with the shuttle’s Canadian-built remote manipulator system, or robotic arm, lifting it out of the payload bay, placing it in the “ram clearing” attitude to have atomic oxygen present in low Earth orbit cleanse it of contaminants that could hamper the purity of any produced samples. Plans called for Davis to then release the facility for its two days of free flight. During this process, the astronauts and Mission Control could not properly assess the satellite’s configuration, and troubleshooting efforts led to loss of communications with it. Mission Control instructed the astronauts to berth the facility overnight as ground teams assessed the problem. Engineers traced the problem to a radio frequency interference issue missed due to inadequate preflight testing. The next morning, Davis once again picked up the facility with the robotic arm. The communications issue recurred, but a reboot of the facility’s computer appeared to fix that problem. However, problems cropped up with the satellite’s navigation system, precluding its deployment. All operations and manufacturing occurred with the WSF remaining attached to the robotic arm. Despite this, the facility demonstrated its capabilities by producing five semiconductor films of good quality before Davis berthed it back in the payload bay on flight day seven.
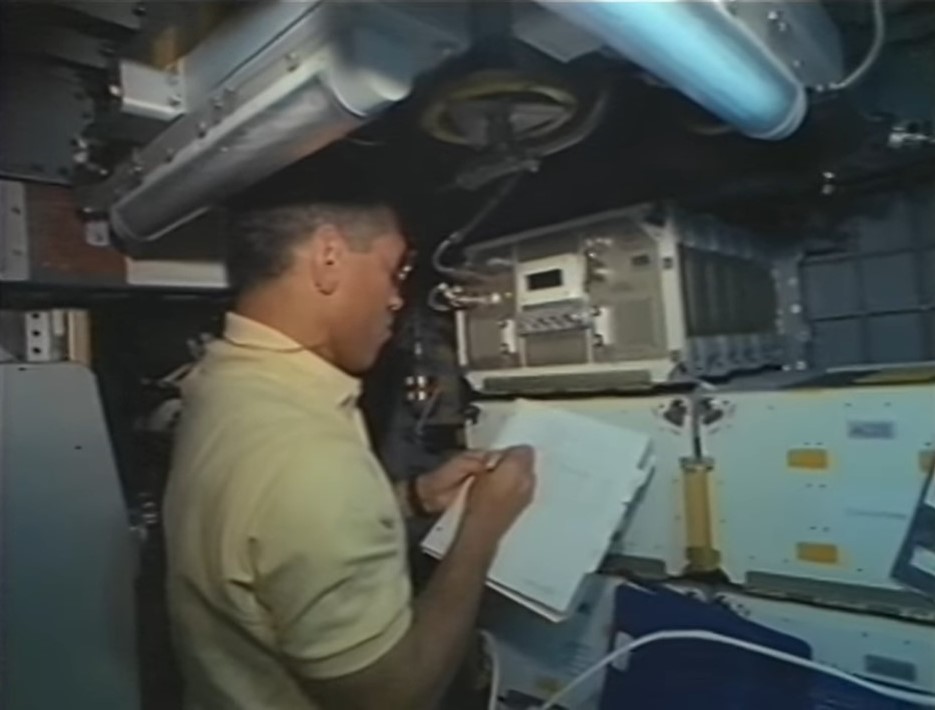
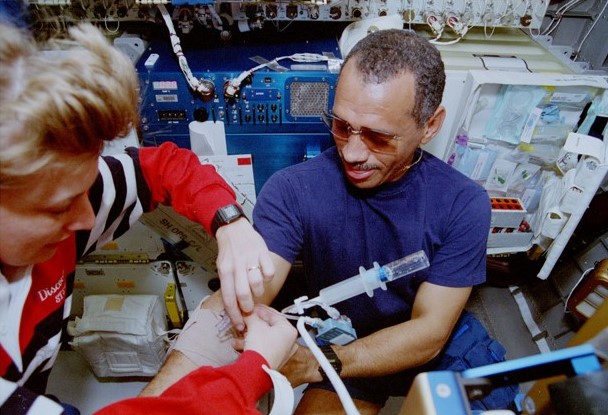


Left: N. Jan Davis takes a peripheral venous pressure measurement on Charles F. Bolden. Middle: Davis operates a fluid processing apparatus, one of the experiments in the Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus. Right: Bolden operates the Organic Separation experiment.
Meanwhile, the astronauts continued with experiments in the middeck and the Spacehab. Another joint investigation called for the measurement of peripheral venous blood pressure. The Spacehab module contained 12 experiments in the fields of biotechnology, materials processing, and microacceleration environment measurement. A thirteenth experiment mounted on the module’s exterior collected cosmic dust particles on aerogel capture cells.
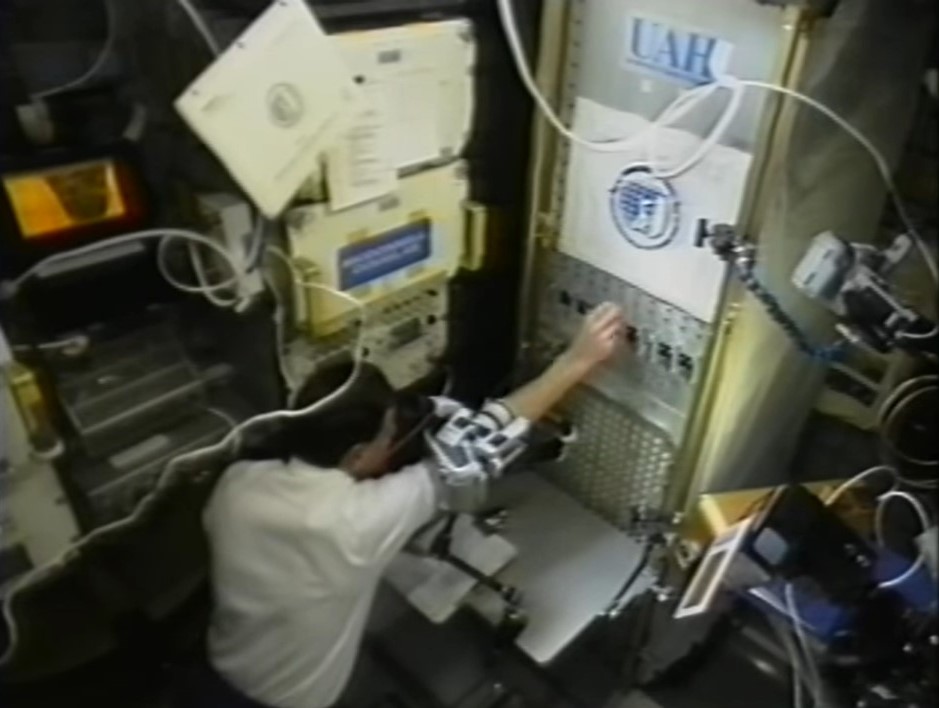
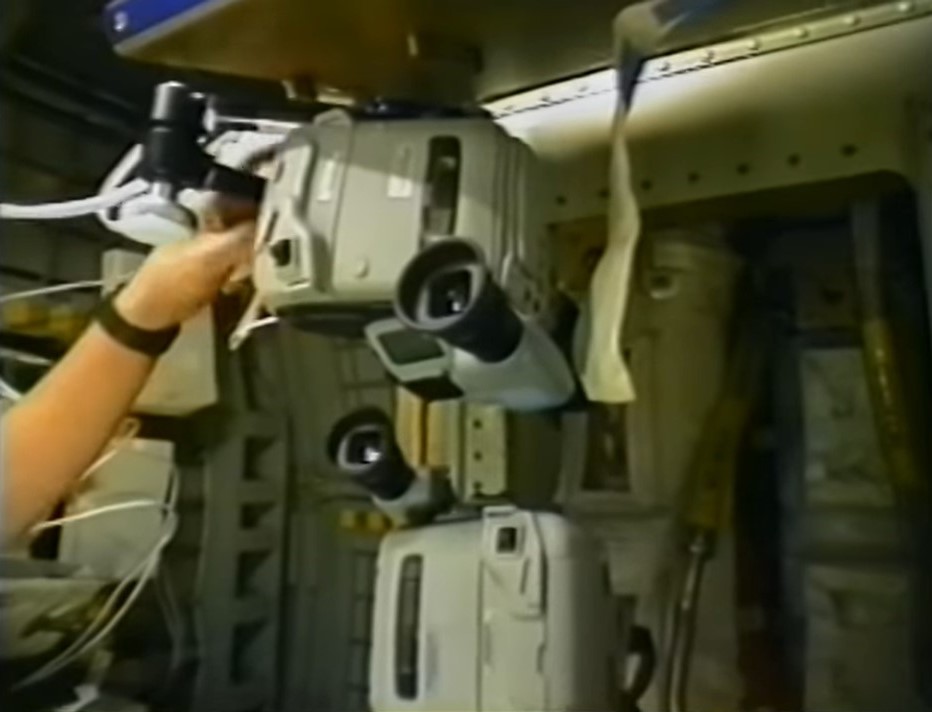
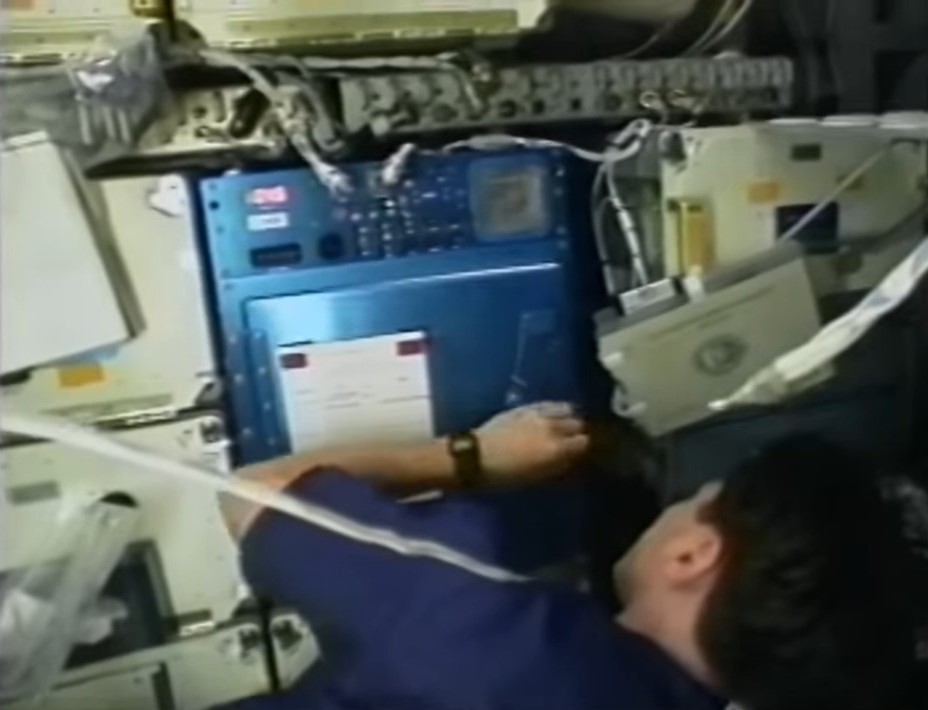




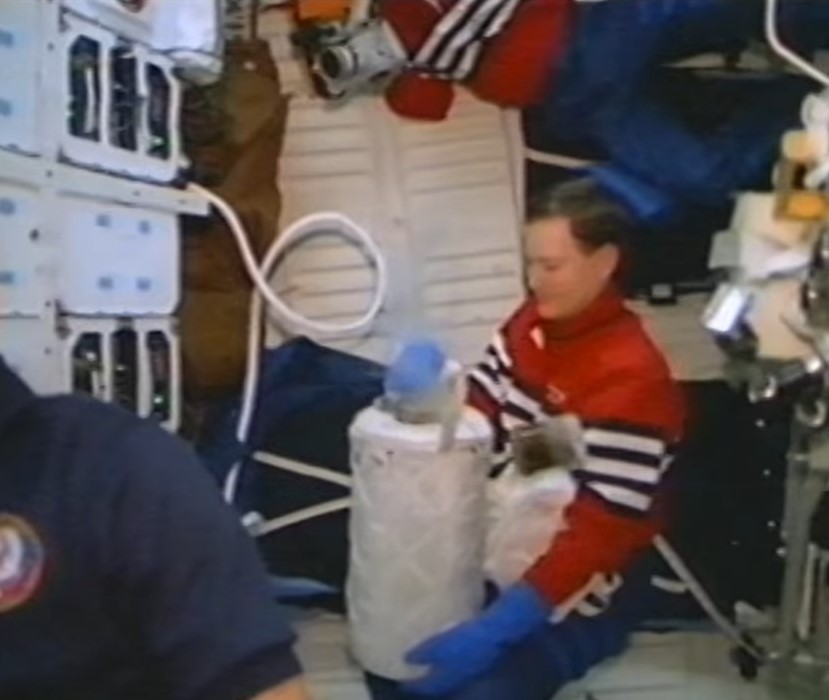
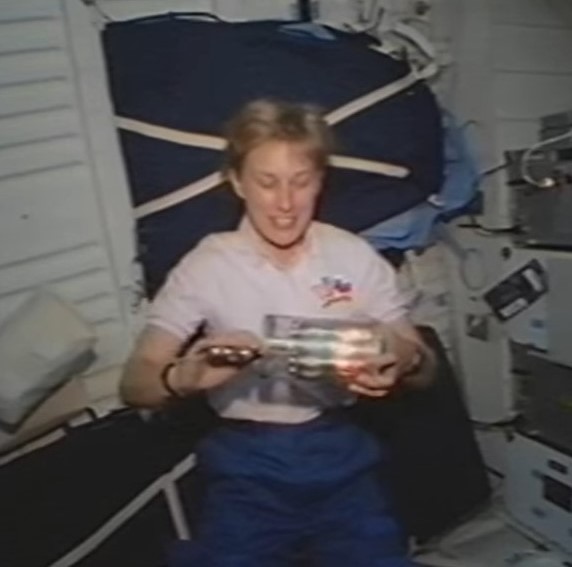
Left: Ronald M. Sega operates the liquid phase sintering experiment. Middle left: Franklin R. Chang-Díaz operates the Space Experiment Furnace. Middle right: The Stirling Orbiter Refrigerator/Freezer technology demonstration. Right: The STS-60 crew enjoys ice cream stored in the freezer.
A technology demonstration on STS-60 involved the test flight of a Stirling Orbiter Refrigerator/Freezer. Planned for use on future missions to store biological samples, on STS-60 the astronauts tested the unit’s ability to chill water containers and provided the crew with a rare treat in space: real ice cream.
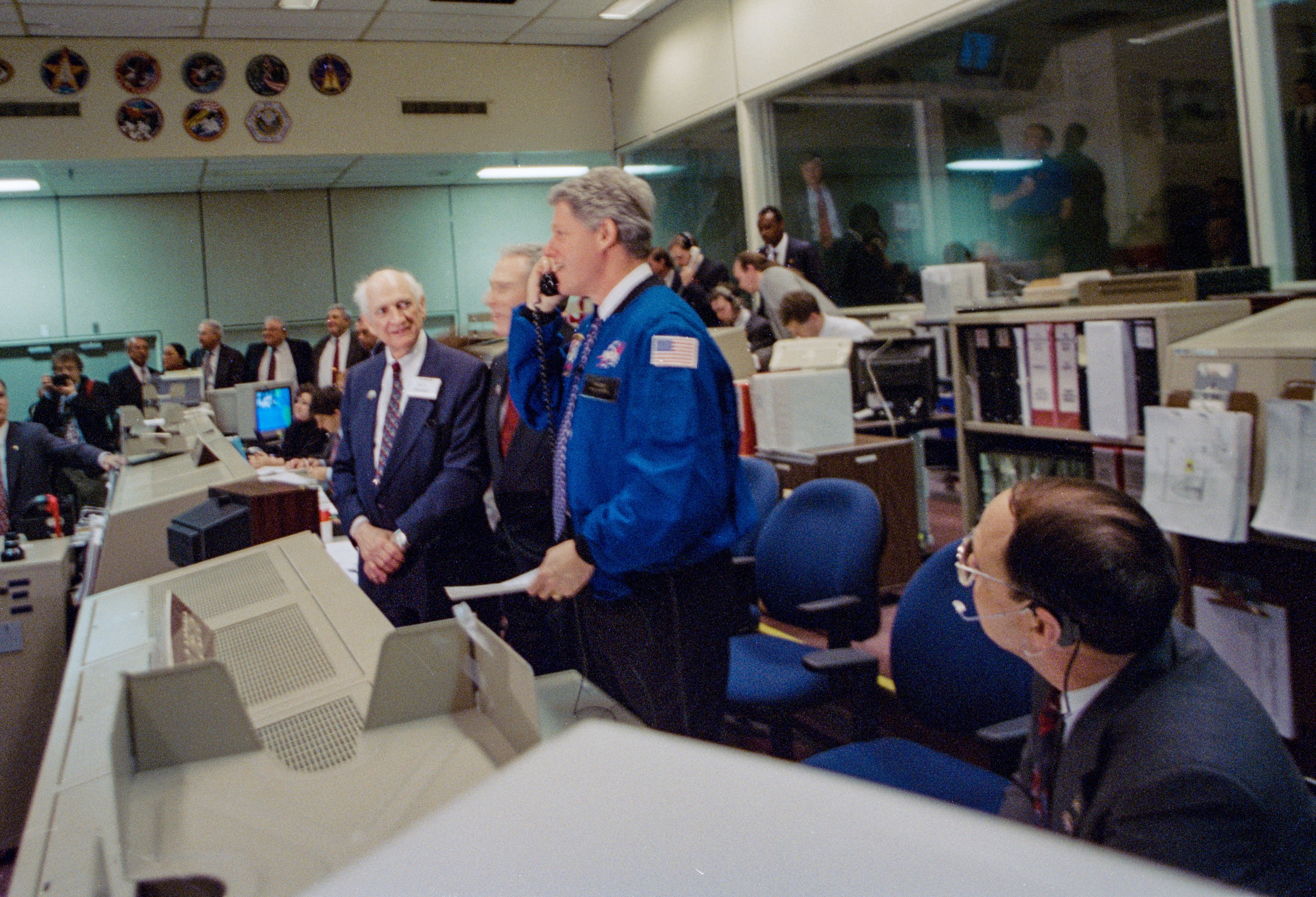


Left: In the Mission Control Center, President William J. “Bill” Clinton chats with the STS-60 crew during his visit to NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Right: The Mir crew and the STS-60 crew talk with each other through the communications link established during the ABC program Good Morning America.
On the astronauts’ fifth day in orbit, President William J. “Bill” Clinton visited Johnson and stopped in the Mission Control Center to talk with them. NASA Administrator Daniel S. Golden and Johnson Director Carolyn L. Huntoon accompanied the President on his tour. President Clinton praised the crew, saying, “I think this is the first step in what will become the norm in global cooperation. And when we get this space station finished…it’s going to be a force for peace and progress that will be truly historic, and you will have played a major role in that.” The following day, the ABC program Good Morning America set up a communications link between Bolden, Davis, and Krikalev aboard Discovery and the three cosmonauts aboard the Mir space station. The two crews chatted with each other and answered reporters’ questions.
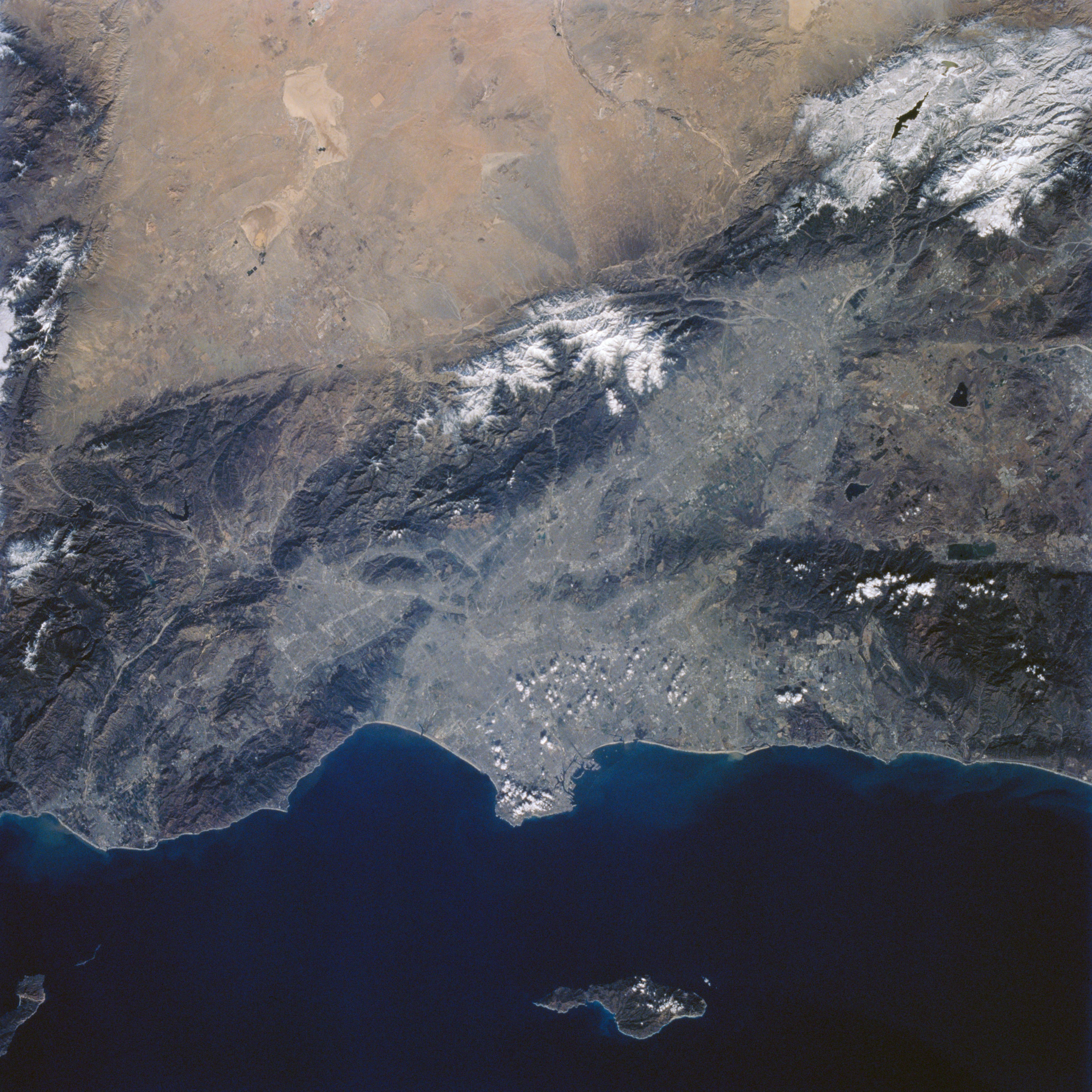
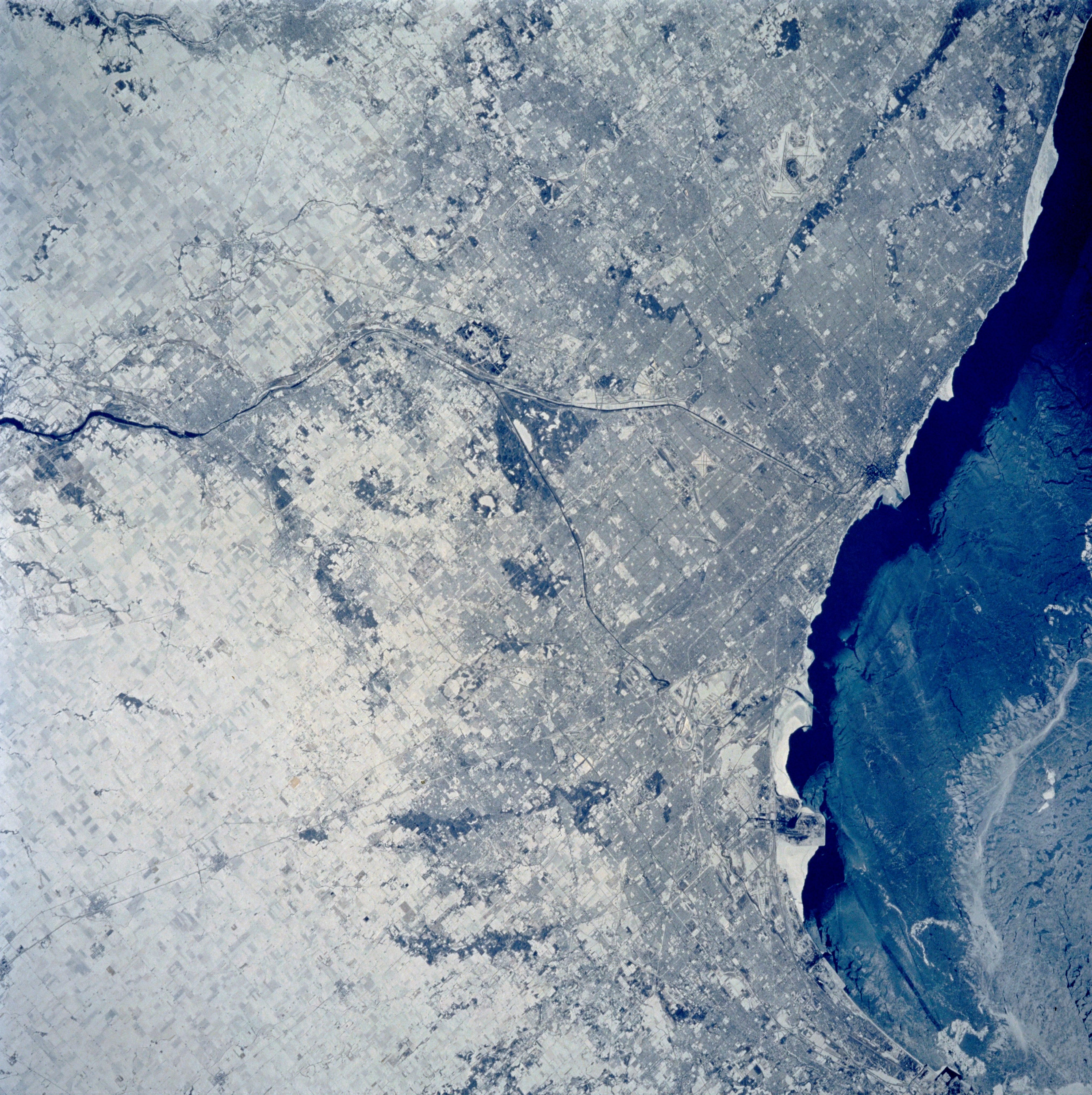
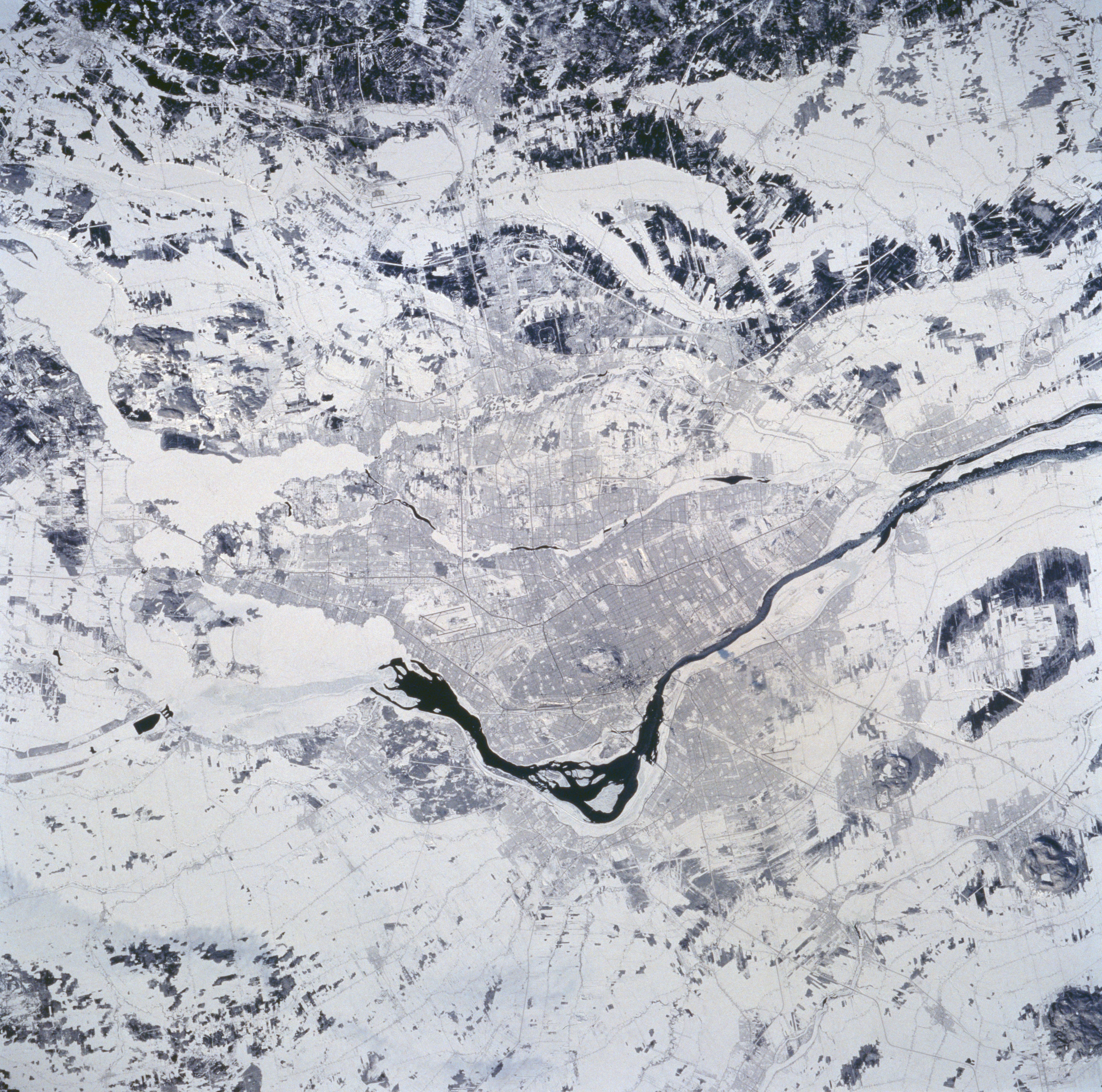




A selection of STS-60 Earth observation photographs of North American cities. Left: Los Angeles. Middle left: Chicago. Middle right: Montréal. Right: New York City.
Every space mission includes astronaut Earth photography, and the 57-degree inclination of STS-60 enabled this crew to image areas on the planet not usually visible to astronauts. Many of the images included spectacular views of snow-covered landscapes in the northern hemisphere winter.
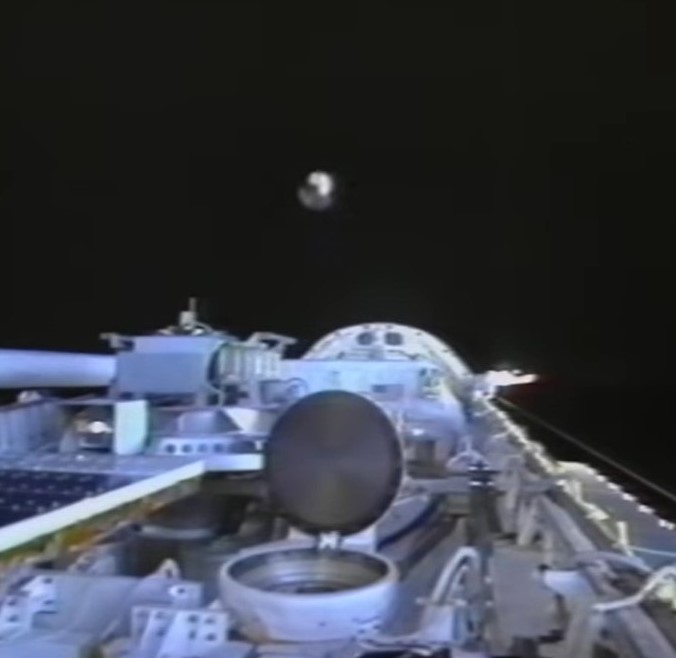
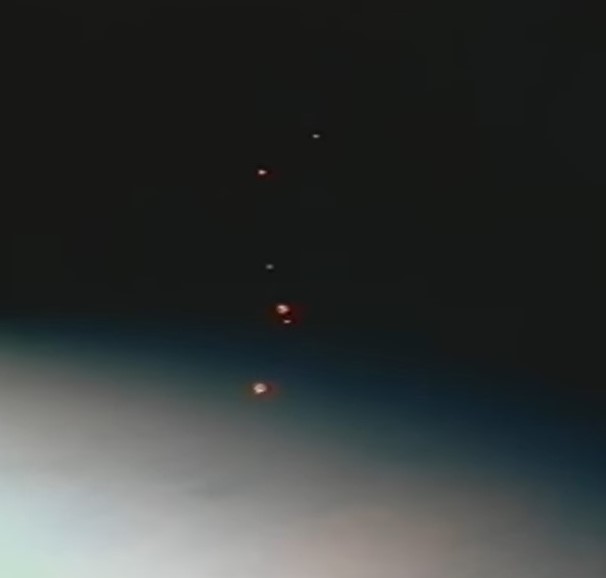
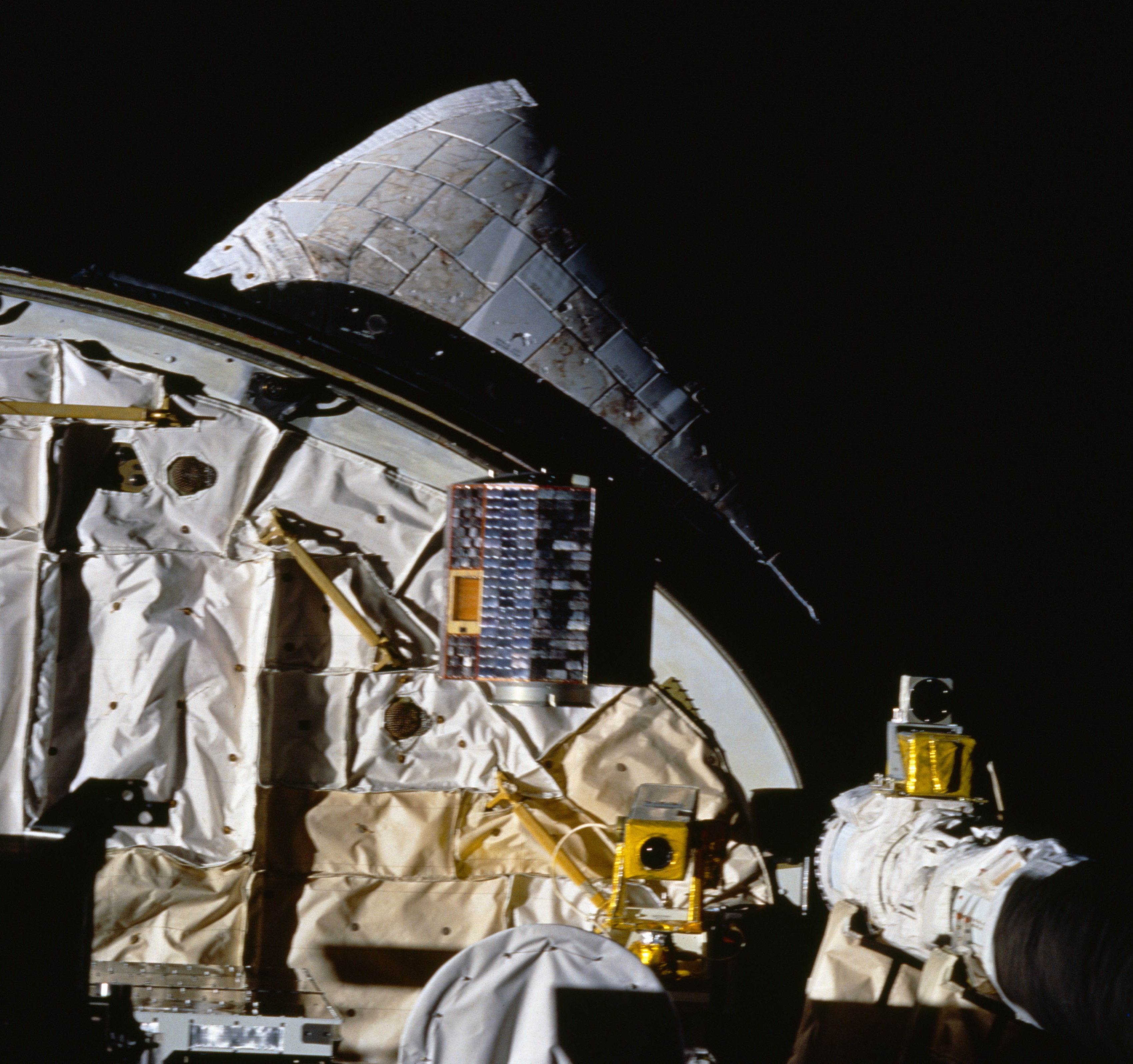



Left: Deployment of one of the six spheres of the Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Spheres experiment. Middle: The six spheres fly away from the shuttle. Right: Deployment of the University of Bremen satellite.
Once the astronauts had stowed the WSF on flight day seven, they could proceed to the deployment of two payloads. The first called Orbital Debris Radar Calibration Spheres consisted of deploying six metal spheres of three different sizes from Discovery’s payload bay. Ground-based radars and optical telescopes observed and tracked the metal spheres to calibrate their instruments. The University of Bremen in Germany provided the second deployable payload. It measured various parameters of its in-orbit environment as well as its internal pressure and temperature as it burned up when it reentered Earth’s atmosphere.
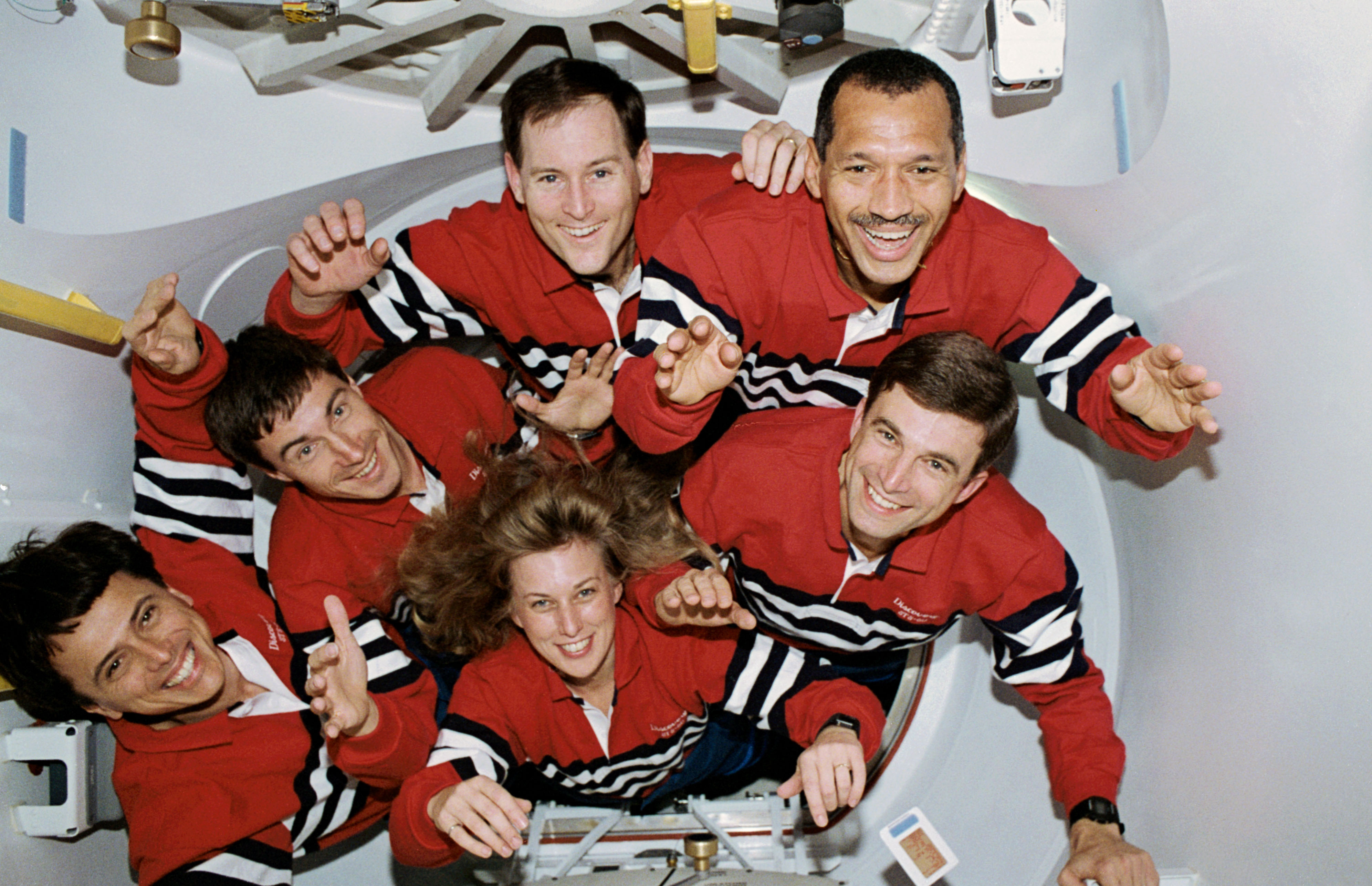

Left: The STS-60 crew members pose near the end of their successful mission. Right: Franklin R. Chang-Díaz, left, and N. Jan Davis close the hatch to the Spacehab module at the end of the mission.
With most of the experiments completed by flight day eight, the astronauts busied themselves with tidying up the middeck and the Spacehab. Bolden and Reightler tested Discovery’s reaction control system thrusters and flight control surfaces in preparation for the deorbit, entry, and landing the following day.
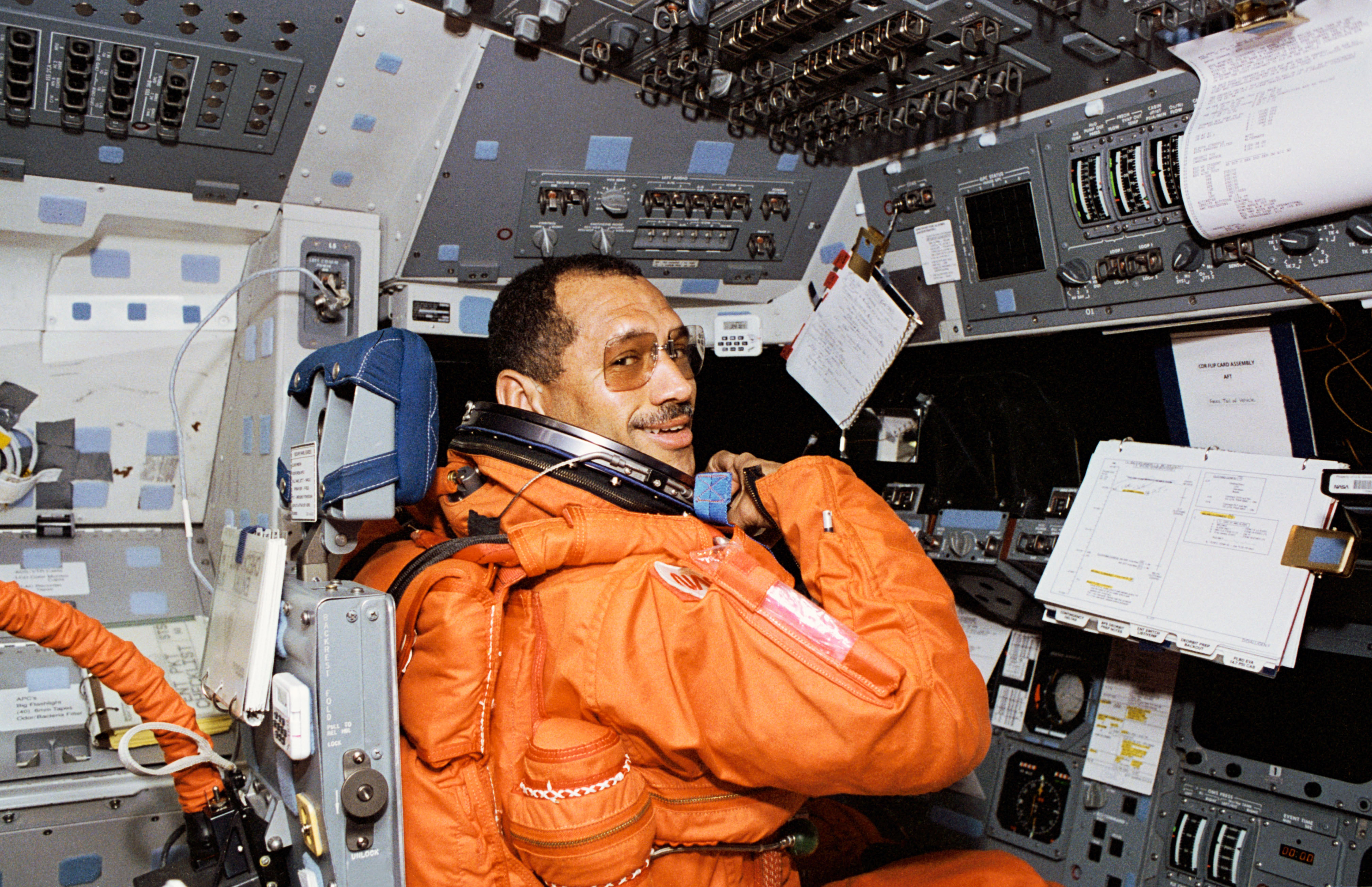
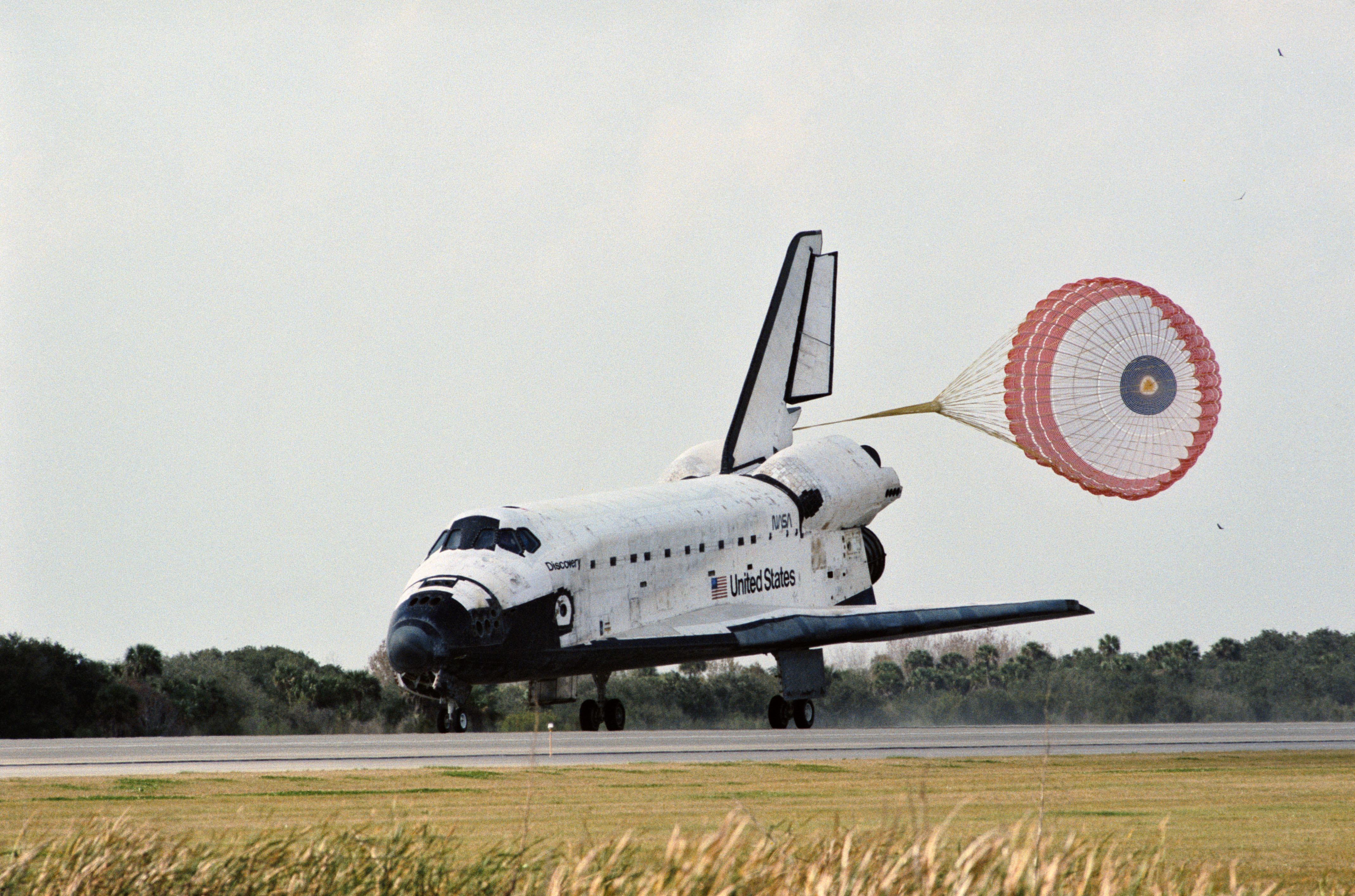


Left: Charles F. Bolden prepares to bring Discovery home. Right: Bolden makes a perfect touchdown at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to conclude STS-60.
On the morning of Feb. 11, the mission’s final day in space, Chang-Díaz and Davis deactivated the Spacehab and closed the hatches to the module. The astronauts donned their launch and entry suits, but NASA delayed their deorbit burn by one orbit due to inclement weather at John F. Kennedy Space Center. Ninety minutes later, they fired the two Orbital Maneuvering System engines to bring them out of orbit and Bolden guided Discovery to a smooth landing at Kennedy, ending the STS-60 mission after 8 days, 7 hours, and 9 minutes, having circled the Earth 130 times.
Enjoy the crew narrate a video about the STS-60 mission. Read Bolden’s and Sega‘s recollections of the STS-60 mission in their oral histories with Johnson’s History Office.
